India's artificial intelligence policy aligns with several Modi government national development initiatives related to equity, self-reliance, and domestic production. In addition, this policy focuses on areas such as education, healthcare, urban development, and agriculture. Bridging language barriers is also a key focus of AI development in India in order to effectively communicate policies and their benefits.
Section:|Agencies|Policies & Strategies|Technology|Education|IN-Taiwan|International Collaboration|Table|
Agencies
- NITI Aayog
- Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY)
- Telecommunication Engineering Centre (TEC)
- Centre for Development of Advanced Computing (C-DAC)
Policies & Strategies
National Strategy for Artificial Intelligence
In June 2018, the Indian government introduced the National Strategy for Artificial Intelligence with the aim of developing “#AIforAll” which creates an AI ecosystem, promotes applications, and addresses the technological gap within the population. NITI Aayog is in charge of implementing this policy, focusing on five major areas: agriculture, healthcare, education, smart cities and infrastructure, and smart transportation. Three execution strategies drive the policy: conducting exploratory AI proof-of-concept projects across various sectors, building a vibrant AI ecosystem, and actively collaborating with experts and stakeholders in different fields.

National Strategy for Artificial Intelligence (Image credit: © INDIAai)
The strategy states that to benefit from large-scale AI deployment, it is essential to address current bottlenecks in India’s AI development, such as the lack of comprehensive professional AI research and applications, a support data ecosystem, collaborative approaches, privacy and security considerations, as well as having high costs but low adoption rates. To overcome these challenges, India has proposed establishing Centres of Research Excellence (CORE) to develop critical technologies by cultivating talent, capabilities, and research in AI.
In October 2024, Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi announced the establishment of three AI Centres of Excellence focusing on healthcare, agriculture, and sustainable cities. These centers are respectively partnered with IIT Delhi, IIT Ropar, IIT Kanpur, and All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS). As such, India’s academic community will lead these three Centres to apply cutting-edge technology in industrial development. (PIB, 2024) (INDIAai, 2024)
In addition, academic organizations throughout Taiwan have collaborated with these institutions for many years. For instance, the National Science and Technology Council funded the National Chung Cheng University (CCU) to establish the “Taiwan-India Joint Research Center on Artificial Intelligence (ITJRC)”. This partnership with the Indian Institute of Technology Ropar focused on research in AI and sustainable cities and lasted from November 2018 to October 2021 and September 2021 to August 2024. In December 2019, National Cheng Kung University signed an MoU with AIIMS to conduct research in dental care and smart manufacturing technology. (MDIC, 2019) (TECC in India, 2019)
National Data Governance Framework Policy
In May 2022, the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) launched a version of the National Data Governance Framework (NDGFP) to “transform and modernize Governments' data collection and management processes and systems”. Through NDGFP, the Indian government aims to standardize and enhance data management used within the government to improve decision-making, program evaluation, and service efficiency. This will strengthen government data governance and drive India's digital economy forward by acting as a catalyst for artificial intelligence, the analytics ecosystem, and the start-up ecosystem.
Legislation Related to Information Technology
In March 2024, MeitY issued advisory eNo.2(4)/2023-CyberLaws-3 addressing India's Information Technology Act, 2000 and the Information Technology (Intermediary Guidelines and Digital Media Ethics Code) Rules, 2021. The advisory requires technology companies to obtain government approval before releasing any AI products that are not fully tested. Additionally, these products must display warnings to inform users of potential inaccuracies. Intermediaries must also ensure that information sources within their systems are free from bias, discrimination, or any content that could jeopardize electoral processes.
This provision was included because in February, Google’s Gemini chatbot sparked controversy ahead of India’s April elections by responding to a user’s question about whether the Indian Prime Minister was a fascist. As a result, the Indian government will continually strengthen measures to regulate artificial intelligence and large language models by considering future developments in information software. (MeitY, 2024) (CNA, 2023)
Technological Development
BHASHINI
In July 2023, the Indian government launched the National Language Translation Mission (NLTM) due to India’s linguistic diversity, with nearly 122 languages nationwide and 22 officially recognized languages (with distinct scripts) in the country’s Constitution. In terms of digital technology, MeitY will spearhead the development of BHASHINI (भाषिणी), a digital technology initiative aimed at eliminating language barriers and ensuring equitable information access. This initiative seeks to increase the volume of content in Indian languages by creating a national open digital platform that integrates contributions from industry, government, academia, and research sectors into a public database. This enables Indian citizens to conveniently access digital services and benefits in their native languages.
During a December 2023 speech, Prime Minister Modi used BHASHINI in front of an audience for the first time to provide live translation of Hindi (हिन्दी) into Tamil (தமிழ்). Prime Minister Modi also stated that he plans to use this particular AI technology frequently in the future. (CNA, 2023) (INDIAai, 2023)
AIRAWAT
The MeitY funds and manages the AI Research Analytics and Knowledge Dissemination Platform (AIRAWAT), while the Centre for Development of Advanced Computing (C-DAC) of Pune is responsible for setting up and operating the platform’s AI supercomputer.
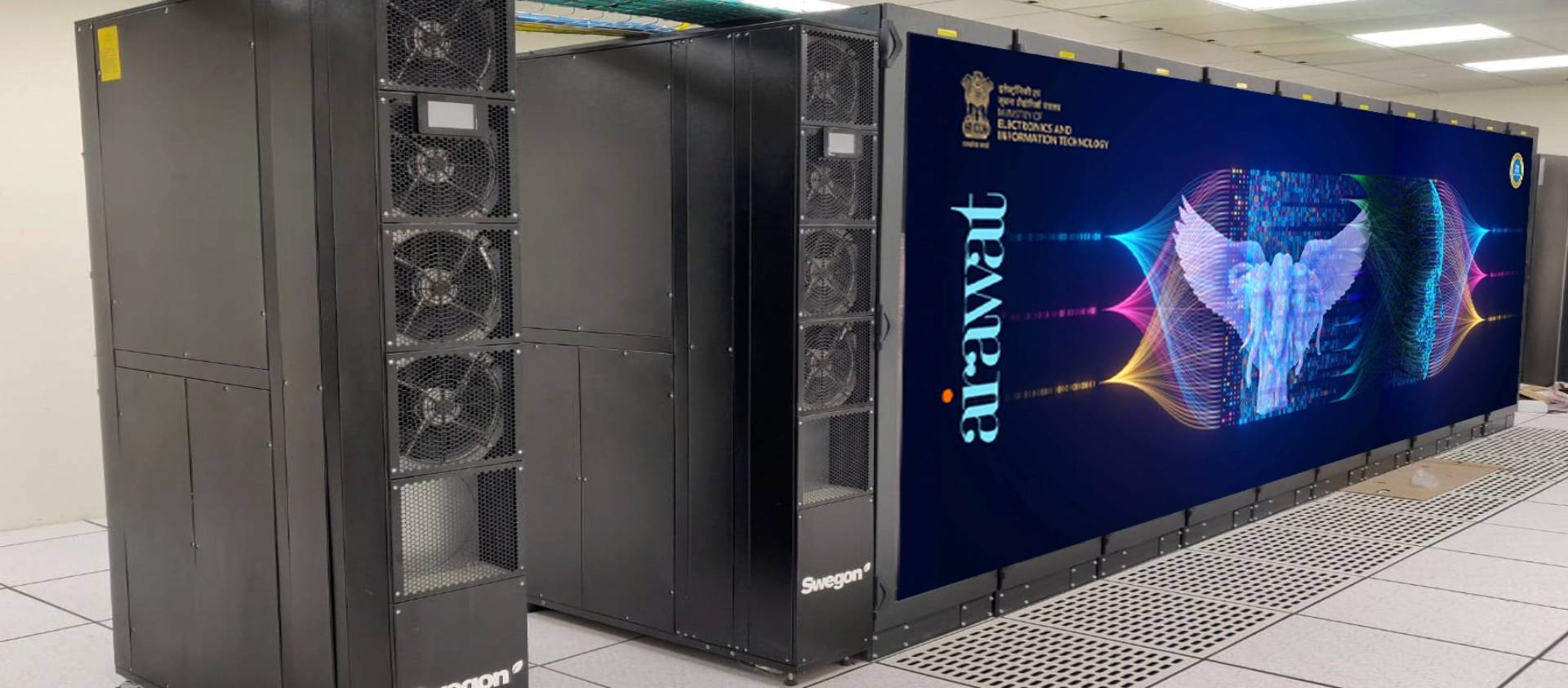

AIRAWAT (Image credit: © C-DAC)
The AIRAWAT PSAI System has a cumulative computing power of 410 AI PF (13.17 PF DP) by integrating cloud computing equipment, PARAM Siddhi-AI and AIRAWAT PoC. With support from the National PARAM Supercomputing Facility (NPSF) and the National Knowledge Network, AIRAWAT serves as a cloud computing platform for big data analytics and integration between India’s AI Centers of Research Excellence, Indian Centres for Transformational AI (ICTAI), and industry, academia, and research institutions. In 2023, AIRAWAT was ranked as the 75th most powerful supercomputer of the TOP500. (C-DAC, 2023)
In implementing the government’s Atmanirbhar Bharat (आत्मनिर्भर भारत) initiative, academia, industry, and startups have been authorized to use AIRAWAT to develop indigenous AI products and solutions. These efforts specifically address India’s unique, significant challenges and complex real-world issues as well as natural language processing and image processing in fields such as education, human resource development, precision agriculture, crop disaster management, financial fraud prevention, precision diagnostics, security surveillance, and supply chain management. (C-DAC, 2023)
BharatGPT
Indian telecom company Reliance Jio Infocomm has partnered with IIT Bombay for an industry-academia collaboration to develop an indigenous AI model, BharatGPT. The vision for this human-centric AI platform aligns with the government’s initiative of “Make AI in India, Make AI Work for India”.
BharatGPT offers several advantages, including India retaining data ownership, domestic experts conducting fine-tuning operations, and collaboration with MeitY’s AI translation system BHASHINI. In addition, BharatGPT integrates voice modality in 14 Indian languages and text modality in 22 Indian languages while supporting capabilities in AI-generated text, speech, and video technology. (INDIAai, 2024)
Anuvaduni
In August 2023, the Indian Ministry of Education established the Anuvadini Foundation, comprising eight nonprofit organizations under the jurisdiction of the All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE). The foundation developed Anuvadini (अनुवादिनी), a multilingual AI translation tool designed to facilitate seamless communication and overcome language barriers for India, a country with thousands of languages. Anuvadini is expected to enhance education, government services, and the development of various industries in India. (ITA, 2024)

Anuvadini (Image credit: © India Taipei Association)
AI4Bharat
IIT Madras has established a research lab to make its datasets, models, and applications available as open-source resources for India's industry, government, academia, and research sectors. In addition, IIT Madras leverages shared resources and collaborates closely with national-level organizations. For instance, IIT Madras has partnered with MeitY - BHASHINI on data and R&D while conducting model training by utilizing Param Siddhi, India's C-DAC high-speed cloud computing infrastructure. The lab also receives funding from international corporations such as Microsoft, Google, and Nvidia.

AI4Bharat (Image credit: © IIT Madras)
Academic Training
Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs)
In October 2023, MeitY established Electronics & ICT Academies (EICT) at several Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs). IIT Kanpur launched a Professional Certificate Course in AI and Machine Learning, covering topics such as emerging technologies, computer science, entrepreneurship, and business. The course spans from foundational theories to core applications and features lectures by distinguished IIT Kanpur alumni and renowned industry experts in AI/ML. Industry insights and skills help students enhance their hands-on projects and capstone projects while strengthening their résumés and providing mock interview assessments. (INDIAai, 2023)
In March 2020, IIT Madras Digital Skills Academy partnered with Forensic Intelligence Surveillance and Security Technologies (FISST) to launch the Career Back 2 Women program, aimed at helping women return to careers in digital industries. The program offers 150-hour training and certification courses in artificial intelligence, machine learning, information security, and big data. Those completing advanced modules also receive guidance in finding employment. To address rapid advances in S&T, the Digital Skills Academy expanded its partnership with NASSCOM to introduce comprehensive courses designed to bridge the skills gap in the latest technologies for experienced students and professionals. The initiative also ensures an efficient division of training responsibilities through academia-industry collaboration. (INDIAai, 2020)
Taiwan-India Cooperation
National Science and Technology Council (NSTC)
The NSTC’s (formerly the Ministry of Science and Technology, MOST) main task under the Executive Yuan's New Southbound Policy has been fostering international research collaboration and advancing the development of the humanities and social sciences. By providing funding to Taiwanese universities and research institutions, the NSTC has established Overseas Science and Technology Innovation Centers (STICs) in New Southbound countries. Through diverse and flexible approaches, these STICs aim to enhance substantial research collaboration and technological innovation exchanges between Taiwan and New Southbound countries.

Taiwan-India Joint Research Center on Artificial Intelligence (ITJRC)
Taiwan-India Joint Research Center on Artificial Intelligence (ITJRC)|Project Period: 2021/09/01 - 2024/08/31
In July 2019, MOST (now the NSTC) approved funding for the Taiwan-India Joint Research Center on Artificial Intelligence (ITJRC). The Center is a partnership between CCU, IIT Ropar, and Chitkara University, with an office set up at IIT Ropar. The initiative actively promotes exchanges and collaboration between Taiwan and India, advances national-level scientific projects, develops critical industrial technologies, and deepens bilateral relations between Taiwan and India. (TECC in India, 2019)
The establishment of this STIC has aimed to serve as a platform for academic research, industry-academia collaboration, and talent cultivation in artificial intelligence. It has expanded existing capacities in research and teaching cooperation between Taiwan and India’s academic and industrial sectors. This Center has also established research laboratories for innovation in AI and FinTech, innovation and entrepreneurship hubs, and international degree programs.
The initiatives of this STIC have deepened exchanges between Taiwan and India, promoted the implementation of international projects, collaborative research projects, short-term international internships, faculty and student exchanges, industry-academia matchmaking between Taiwan and India, and bilateral technical guidance. (MOST, 2019)
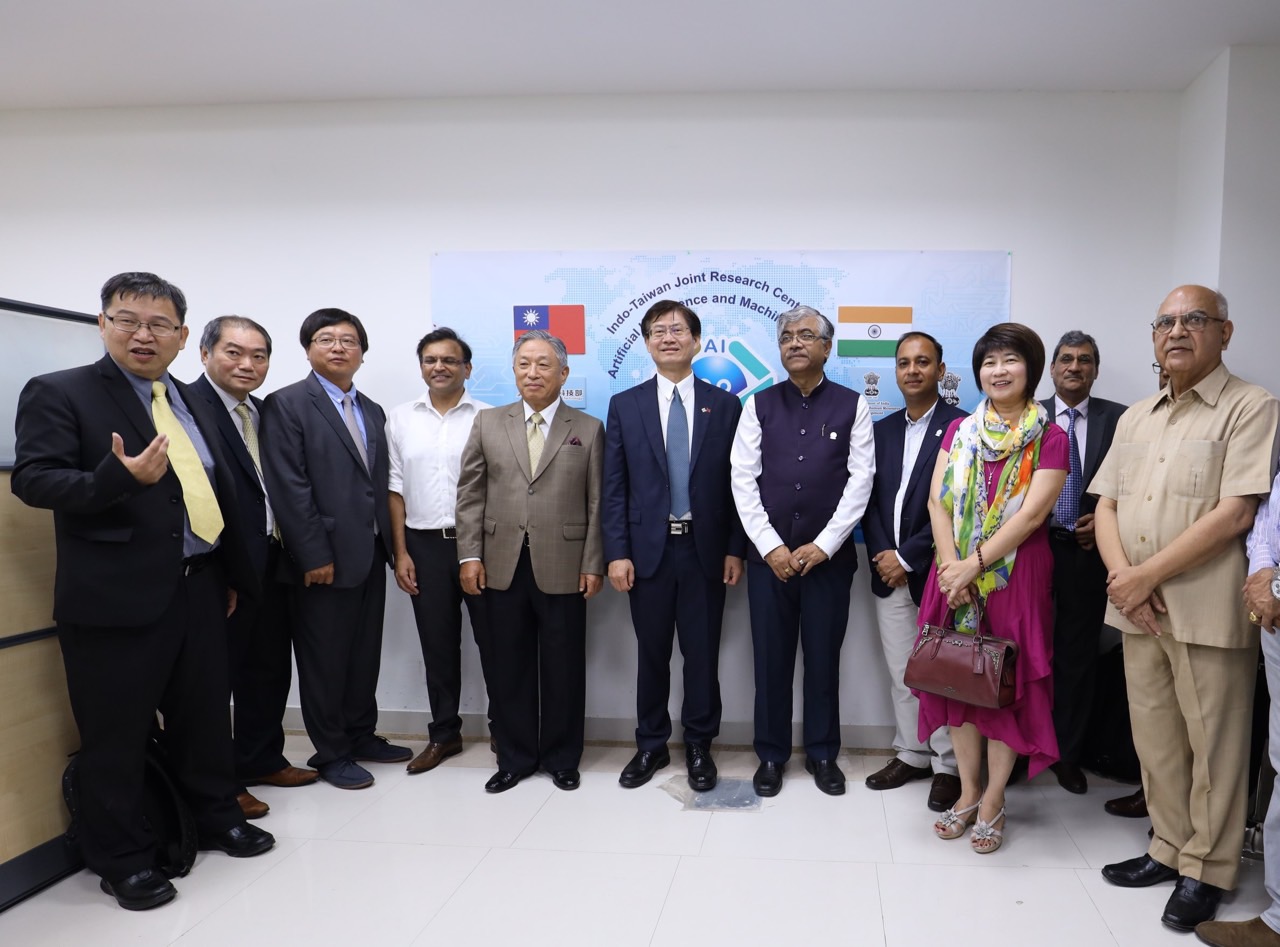

Former MOST Deputy Minister Yu-Chin Hsu leading a delegation to attend the inauguration ceremony of the Taiwan-India Joint Research Center on Artificial Intelligence (Photo Credit: © MOST (now the NSTC)
In 2021, CCU’s Taiwan-India Joint Research Center on Artificial Intelligence – II focused on developing Sustainability and Digital Transformation for Smart Cities, with three main pillars: smartification, digitalization, and sustainability. Through field applications and solutions tailored to India’s specific needs, the Center integrated Taiwan’s forward-looking AIoT and environmental protection technologies to help address India’s pressing environmental challenges.
The Taiwan-India Joint Research Center on Artificial Intelligence has achieved numerous outcomes, including collaborating with the Sri Ramaswamy Memorial Institute of Science and Technology (SRM) to develop Smart Epidemic Prevention Systems. These systems feature technologies such as facial recognition, mask detection, temperature sensing, and social network analysis. In addition, these systems have been implemented on campuses and in local hospitals in India, significantly contributing to the health and safety of faculty, staff, and students.
CCU and SRM have jointly published three academic papers related to smart epidemic prevention. Additionally, this partnership has successfully established a model for international academic collaboration by facilitating preliminary research achievements in areas such as smart bamboo recognition and precision agriculture, as well as precision marketing and recommendation systems. (CCU SDGs, 2021) (CCU, 2022)
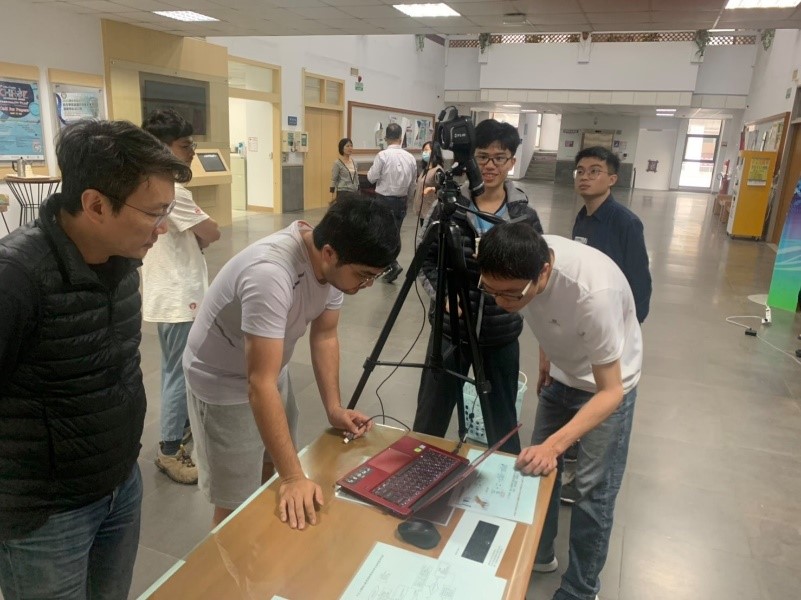

A CCU team developed a “Facial Recognition System” with a thermal imaging camera (Photo Credit: © CCU/MOST, 2020)
Taiwan-India Living Lab on Big Data Analytics
In September 2022, CCU’s Taiwan-India Joint Research Center on Artificial Intelligence and SRM Institute of Science and Technology (SRMIST) jointly established the Taiwan-India Living Lab on Big Data Analytics. With a bilateral research focus on smart healthcare, the Living Lab aims to build an international network for smart healthcare.
Professor Pao-Ann Hsiung, the project’s principal investigator, stated that the country’s healthcare resources have underserved its current population of 1.4 billion for many years. In the future, the Living Lab will integrate CCU’s robust research capabilities in medical image recognition technology, data science analysis, and precision medicine to help India address its current shortages in healthcare resources. In addition, the Living Lab will also facilitate the joint publication of research papers and applications for bilateral collaboration projects. Its establishment is expected to drive innovative cooperation models between Taiwan and India in the field of smart healthcare. (CCU, 2022) (TECC in India, 2022)
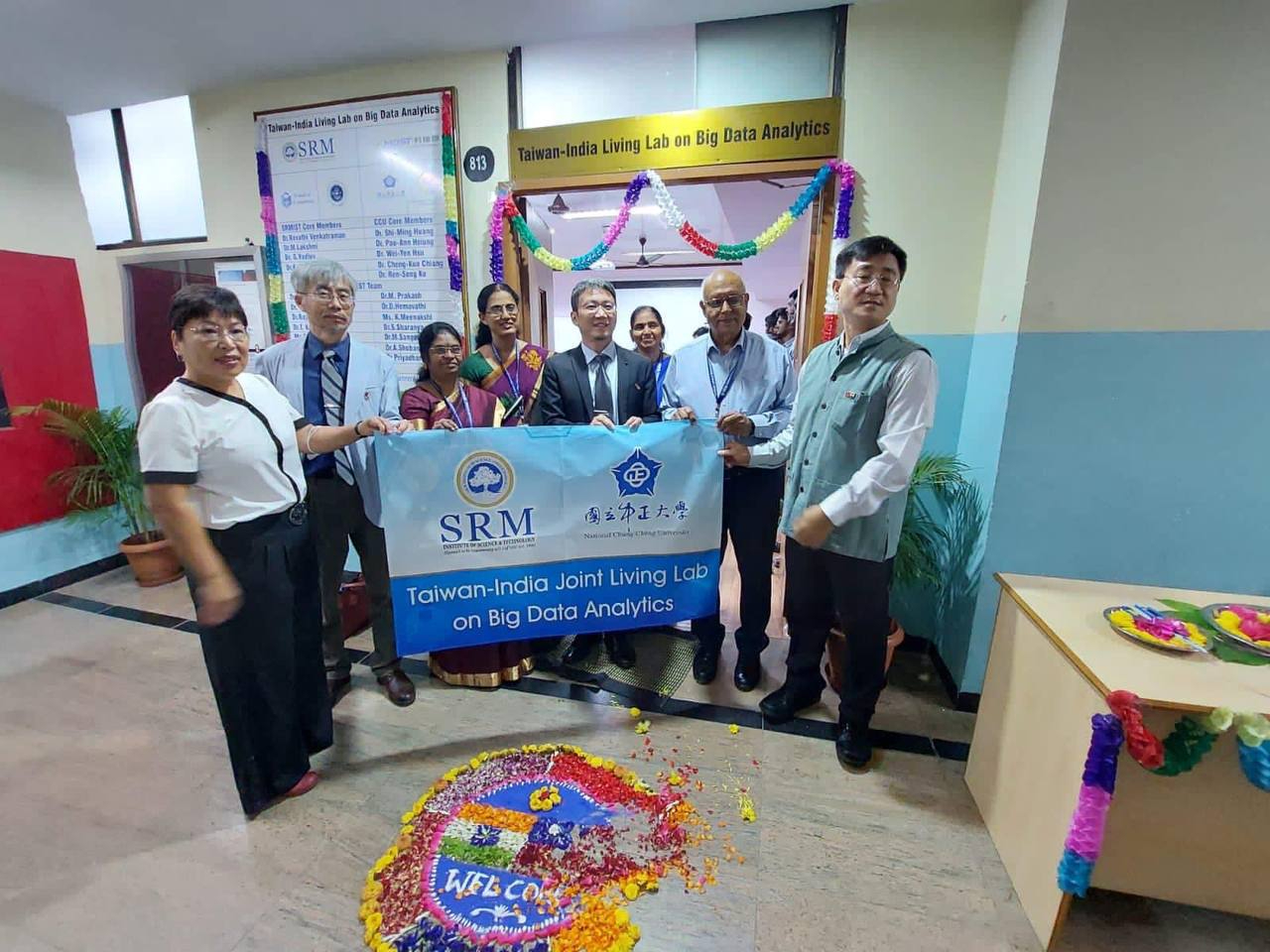

Unveiling Ceremony for the Taiwan-India Living Lab on Big Data Analytics (Photo Credit: © Taipei Economic and Cultural Center in India)
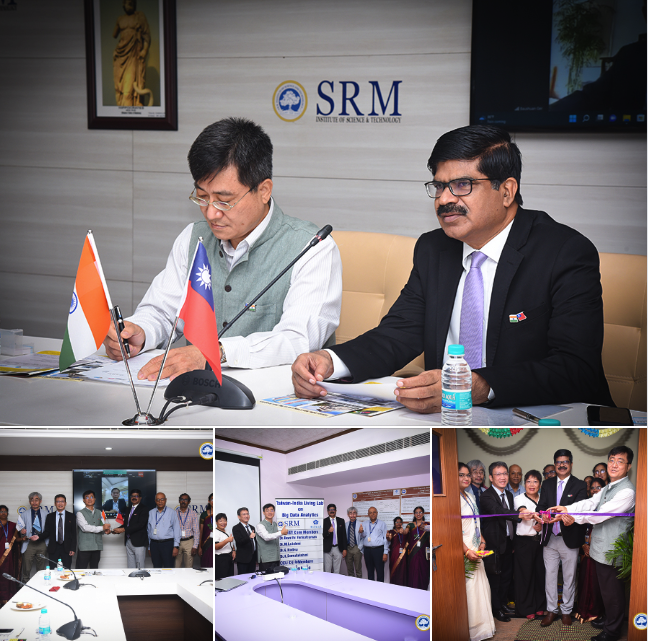

The former Head of the NSTC’s Science and Technology Division in India, the President of SRMIST, and the Director of the Taiwan-India Joint Research Center on Artificial Intelligence attended the inauguration ceremony of the Taiwan-India Living Lab on Big Data Analytics. (Photo Credit: © SRMIST)
Sustainable Smart City Research Laboratory
In September 2022, CCU’s Taiwan-India Joint Research Center on Artificial Intelligence and Chitkara University jointly established the Sustainable Smart City Research Laboratory. This four-year project in collaboration with the Chandigarh Administration, aims to drive international data analysis and applications for sustainable smart cities.
From its inception, the lab has established steadfast connections with India’s industry, government, and academic sectors. Leveraging research and development experience, the Laboratory seeks to rapidly create benefit for more cities while aligning with Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s 2015 announcement to develop 100 smart cities, with Chandigarh as a key focus. The project also includes well-designed social infrastructure and significant investments in smart transportation and lighting. (CCU, 2022)
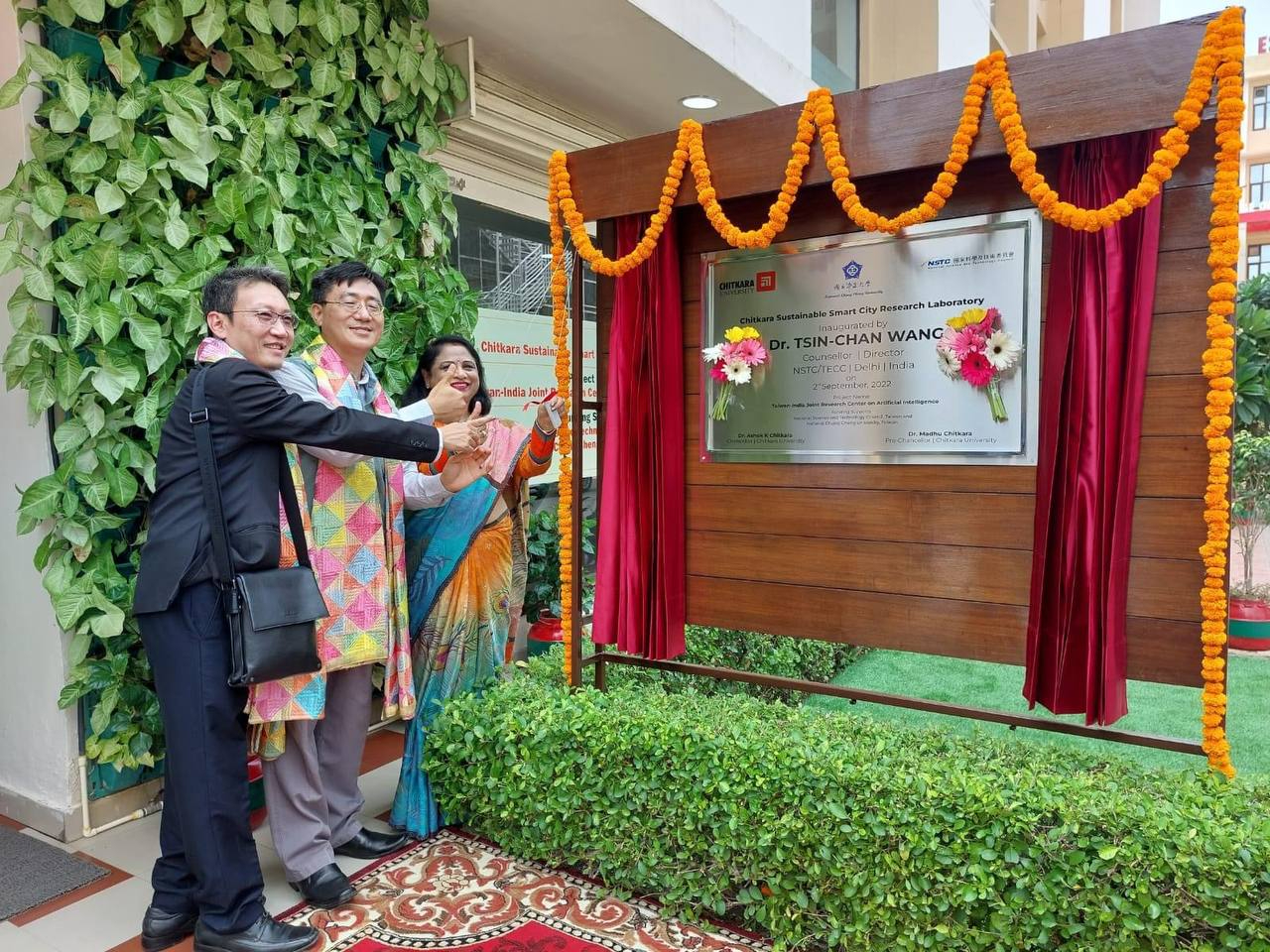
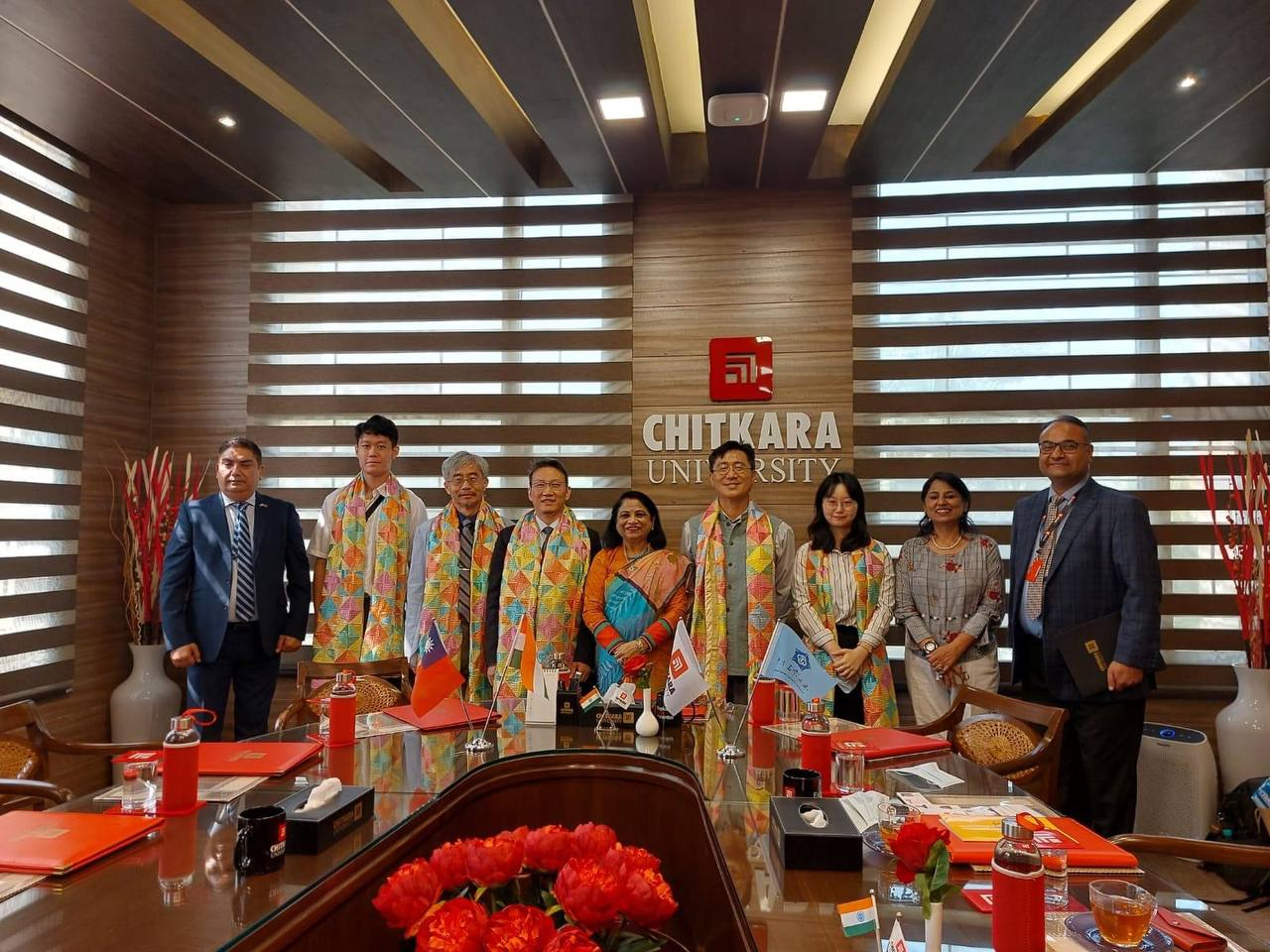


Unveiling ceremony for the Sustainable Smart City Research Laboratory
(Photo Credit: Taipei Economic and Cultural Center in India, 2022)
Artificial Intelligence/ Cybersecurity
In May 2023, the Indo-Taiwan Bilateral Workshop on Cyber Security was held at IIT Jammu, focusing on the theme of “Digital Security”. Discussions included leveraging AI to enhance cybersecurity defenses and methods to protect AI systems from attacks. Both India and Taiwan aim to build cybersecurity defenses through AI because both countries face challenges from external cyberattacks and misinformation.
Taiwan's participants included Taiwan Representative Office in India Science and Technology Division Director Dr. Chin-Tsan Wang, as well as a total of seven cybersecurity specialists from National Chung Cheng University, National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University, National Taiwan University of Science and Technology, and National Cheng Kung University.
This workshop was organized following the resolution of the 11th Meeting of the India-Taiwan Joint Committee on Cooperation in Science and Technology in 2022 between the NSTC and India’s Department of Science & Technology. (CNA, 2023)
International Collaboration
Meta
In July 2023, INDIAai signed an MoU with the US tech company Meta to apply their open-source AI models to India’s AI ecosystem. This partnership is expected to complement India’s digital leadership and the tech industry’s openness to innovative AI. (INDIAai, 2023)
In addition, INDIAai, launched by MeitY, has served as a hub for national AI policies and research while housing one of the country’s largest data repositories. Through close collaboration with Meta, INDIAai ensures that AI is tailored to India’s unique needs by providing industry, government, and academia with advanced technologies. This partnership has also strengthened India’s digital leadership and is anticipated to create significant opportunities for social and economic development.
The initial phase of collaboration between INDIAai and Meta has focused on creating Indian Datasets with an emphasis on low-resource languages. By utilizing Meta's AI language models, such as Llama, Massively Multilingual Speech (MMS), and No Language Left Behind (NLLB), the partnership aims to enable translation and large language model applications. This initiative is expected to enhance social inclusion while strengthening the service capabilities of the government.
Both parties are also considering establishing a Center of Excellence to contribute to the training of AI talent while enhancing professional knowledge in India’s emerging technology and AI. (INDIAai, 2023) (PIB, 2023)
Microsoft
In Bangalore, India’s premier technology hub, Microsoft Research India partnered with Microsoft teams worldwide to launch Siksha Copilot (शिक्षा / Education). This partnership aims to enhance the capabilities of teachers while improving student learning outcomes throughout the country. Siksha Copilot uses AI to assist teachers in planning lessons tailored to their students, diversifying educational materials, assigning homework, and reducing preparation time. This helps create an engaging classroom environment by facilitating interaction between students and teachers.
Siksha Copilot utilizes UniVersal Empowerment with Large Language Models (VeLLM). This technology, which Microsoft Research India developed, supports both English and Kannada (ಕನ್ನಡ), the official language of Karnataka state, whose capital is Bangalore. (Microsoft Research Blog, 2023)
In February 2024, Microsoft CEO Satya Nadella shared how tools like Siksha Copilot are making a tangible impact on mainstream education and student engagement in class. The Sikshana Foundation reported that AI has made classrooms more dynamic while reducing lesson planning time from one hour to under 15 minutes. Currently, 30 schools and 30 teachers in Karnataka are participating in the partnership. Moreover, this project primarily uses local languages for instruction, with only six teachers conducting classes in English. The foundation aims to expand the program to 100 schools by the end of the academic year. (Satya Nadella, 2024) (Microsoft News, 2024) (INDIAai, 2024) (Firstpost, 2024)
Microsoft has also led the development of Jugalbandi, an AI chatbot that leverages Microsoft Azure’s machine learning technology, OpenAI’s large language models, MeitY’s BHASHINI, and Indian government databases. In addition, Jugalbandi addresses the challenges posed by India’s linguistic diversity that hinder communication and development. As a public-private collaborative platform, Jugalbandi enables Indian citizens to understand government policies, rights, and benefits. Jugalbandi functions as an AI translation tool for Indian languages on mobile devices and currently supports 10 Indian languages and 171 government projects. Additionally, Jugalbandi has been applied in various sectors, including the Department of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare, the government of Andhra Pradesh, the High Court of Karnataka, and the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI). Jugalbandi benefits millions of Indian citizens by facilitating access in areas such as justice, education, and healthcare.
Global Partnership on Artificial Intelligence (GPAI)
(New Southbound partner countries—Australia, India, New Zealand, and Singapore—are members of GPAI)*
The Global Partnership on Artificial Intelligence (GPAI), an OECD-led project, has brought together experts from 29 international partners (28 countries plus the EU) across a diverse range of sectors ranging from science and industry to government and civil society. GPAI upholds the principle that AI development should align with “human-centric” values such as human rights, diversity and inclusion, innovation, and economic development while also striving to meet UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Under this framework of shared values, GPAI invests in cutting-edge AI research and applications to bridge the gap between theory and practice. In its initial phase, GPAI experts collaborated with four AI-themed working groups:
- Responsible AI Working Group
- Data Governance Working Group
- Future of Work Working Group
- Innovation & Commercialization Working Group
GPAI Summit 2023 (Image credit: © MeitY)
In December 2023, the GPAI New Delhi Summit was held in New Delhi, India. This event brought together numerous stakeholders to highlight the latest advancements in AI technology, policy frameworks, ethics, and contributions from industry, government, academia, and research sectors. The summit also explored ways to promote AI accessibility, particularly among youth and students. Additionally, the summit brought together key initiatives from the UN Advisory Group on AI and the major outcomes of the AI Safety Summit 2023.
According to the 2023 GPAI Ministerial Declaration, member countries reached a consensus to jointly promote safe and trustworthy artificial intelligence and pledged to support sustainability in GPAI projects. Prime Minister Modi also called on countries across the globe to work together in formulating an international framework for the ethical use of AI.
AIRAWAT supercomputer and the National Programme on Artificial Intelligence (NPAI) have played critical roles in the development of India’s AI ecosystem. In the future, India aims to become a global hub for AI innovation. (PIB, 2023)
Quadrilateral Security Dialogue (Quad)
(New Southbound partner countries—Australia and India—are members of the Quad)*
The Quad is a cooperative framework among the US, Japan, India, and Australia. The “Quad spirit” aims to foster the universal values of freedom, openness, inclusivity, and democracy by facilitating shared prosperity and solidarity in the Indo-Pacific region. As a key bridge for the US in the Indo-Pacific, the Quad promotes collaboration in technology, economics, and security. Artificial intelligence is one of the Quad’s main focal points, with each member leveraging its strengths to deepen and expand cooperation. This includes partnerships across industry, government, and academia to achieve the Quad's goals for cooperation in advanced technology.
During the Quad Leaders’ Summit in September 2021, key discussions highlighted the establishment of Technical Standards Contact Groups that focus on the formulation of standards and standardized research for advanced communication technologies and artificial intelligence. (The White House, 2021) (MEA, 2021)
In line with the “Quad spirit,” like-minded democratic nations should engage in international technological collaboration. Quad-led cooperation in AI aims to create an open and secure technological ecosystem. These efforts will help counter authoritarian regimes' disruptive activities in the Indo-Pacific region, particularly the malicious misuse of AI for authoritarian surveillance, censorship, repression, and the dissemination of disinformation. (CSET, 2022)
India's Policy on Artificial Intelligence
| Agency | Policy, Strategy, Project & Initiative |
|---|---|
| NITI Aayog | |
|
Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) |
|
|
Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) |
|
|
Telecommunication Engineering Centre (TEC) |
Study Paper on Artificial Intelligence (AI) Policies in India - A Status Paper |
| Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) |
National Language Translation Mission BHASHINI (भाषिणी) |
|
Ministry of Education (MoE) |
|
|
Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) Meta |
|
|
Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) Centre for Development of Advanced Computing (C-DAC) |
AIRAWAT (AI Research Analytics and Knowledge Dissemination Platform) |
|
Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) Digital India INDIAai CoRover® |
|
|
Microsoft / Microsoft Research OpenAI OpenNyAI Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) |
|
| Microsoft Research India | |
|
National Science and Technology Council (NSTC) National Chung Cheng University (CCU) Indian Institute of Technology Ropar (IIT Ropar) |
Taiwan-India Joint Research Center on Artificial Intelligence |
|
National Chung Cheng University (CCU) SRM Institute of Science and Technology (SRMIST) |
|
|
Taiwan-India Joint Research Centre on Artificial Intelligence (ITJRC) National Chung Cheng University (CCU) Chitkara University |
Keywords: #India #Artificial_Intelligence
Reference / Sources:
Indian Sources
-
INDIAai (2024.10) Prime Minister hails the establishment of three AI Centres of Excellence
-
Press Information Bureau (2024.10) Prime Minister lauds establishment of three AI Centres of Excellence (CoE)
-
ETCISO (2024.04) MeitY advisory for Gen AI regulation
-
ETCISO (2024.03) Seek nod before launching AI models in India: Centre to social media platforms
-
MeitY (2024.03) eNo.2(4)/2023-CyberLaws-3
-
Hindustan Times (2024.03) Under-testing AI models must get govt permission before deployment: MeitY
-
INDIAai (2024.08) ISRO-IIRS to offer a free 5-day course on AI and ML
-
INDIAai (2024.02) Microsoft is planning to extend its Shiksha CoPilot to over 100 schools in India
-
INDIAai (2024.01) Reliance Jio and IIT Bombay to launch Bharat GPT Program
-
INDIAai (2023.12) PM Modi used the AU tool Bhashini while delivering his speech in Varanasi
-
Press Information Bureau (2023.12) Year End Review 2023 of Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology
-
Press Information Bureau (2023.12) Three-Day GPAI Summit concluded today at Bharat Mandapam!
-
INDIAai (2023.12) Exploring the GPAI Summit 2023 events: Day 3
-
INDIAai (2023.12) Exploring the GPAI Summit 2023 events: Day 2
-
INDIAai (2023.12) Exploring the GPAI Summit 2023 events: Day 1
-
INDIAai (2023.12) MeitY to organize GPAI summit 2023, here is everything you should know about GPAI
-
INDIAai (2023.12) Microsoft’s India Development Centre celebrates 25 years of technological innovation and excellence
-
INDIAai (2023.11) Microsoft Research India launches ‘Siksha Copilot’ to enhance learning using AI-powered teaching support
-
INDIAai (2023.10) IIT Kanpur launches Professional Certificate Course in AI and ML
-
INDIAai (2023.07) India AI and Meta sign an MoU to establish a framework in AI & Emerging Technologies
-
INDIAai (2023.05) Quad AI: Assessing AI-related collaboration between the United States, Australia, India and Japan
-
MeitY (2023.04) The Information Technology (Intermediary Guidelines and Digital Media Ethics Code) Rules, 2021
-
NITI Aayog (2023.03) National Strategy for Artificial Intelligence [.pdf]
-
Chitkara University (2022.09) Sustainable Smart City Research Lab under Indo-Taiwan Partnership inaugurated
-
MeitY (2022.05) National Data Governance Framework Policy (Draft) [.pdf]
-
Ministry of External Affairs, India (2021.09) Fact Sheet: Quad Leaders’ Summit
-
INDIAai (2021.03) India, Taiwan explore AI technology cooperation
-
INDIAai (2020.03) IIT-M launches digital course to reskill women in AI
-
IIT Kanpur Professional Certificate Course in AI and Machine Learning
-
IIT Madras Career Back To Women (CB2Women)
-
Centre for Development of Advanced Computing AIRAWAT PoC
-
Centre for Development of Advanced Computing AIRAWAT-PSAI
-
Centre for Development of Advanced Computing PARAM Siddhi-AI
-
Centre for Development of Advanced Computing National PARAM Supercomputing Facility (NPSF)
-
AI4Bharat Building AI for India!
-
印度電子通訊部 MeitY Information Technology Act 2000
Foreign Sources
-
Council on Foreign Relations (2022.06) The Future of the Quad’s Technology Cooperation Hangs in the Balance
-
Center for Security and Emerging Technology (2022.05) Quad AI: Assessing AI-related Collaboration between the United States, Australia, India, and Japan
-
The White House (2021.09) Fact Sheet: Quad Leader’s Summit
-
OECD Observer (2020.03) What are the OECD Principles on AI?
-
OECD Legal Instruments (2019.05) Recommendation of the Council on Artificial Intelligence
Other Source
-
The Economic Times (2024.03) MeitY approval must for companies to roll out AI, generative AI models
-
Satya Nadella on X (2024.02) It was awesome seeing firsthand today this example of how Indian educators are applying this next generation of AI to give time back to teachers and deliver more engaging lesson plans for students.
-
Firstpost (2024.02) Microsoft to extend its educational AI for India, Shiksha CoPilot, to over 100 schools
-
Microsoft News (2024.02) India’s schoolteachers are drafting better lesson plans faster, thanks to a copilot
-
Microsoft News (2023.12) With help from next-generation AI, Indian villagers gain easier access to government services
-
The Economics Times (2023.12) GPAI Summit 2023: 29 nations adopt New Delhi resolution
-
Microsoft Research Blog (2023.10) Teachers in India help Microsoft Research design AI tool for creating great classroom content
-
CoRover (n.d.) About BharatGPT
-
Jugalbandi (2023) About Jugalbandi
-
Ministers of the Global Partnership on Artificial Intelligence (GPAI) (2023.12) 2023 GPAI Ministerial Declaration
Domestic Sources
-
印度台北協會 ITA (2024.07) Anuvadini 是印度開發的多語言人工智慧翻譯工具,讓擁有上千種語言的印度人能跨越語言的藩籬達到無障礙溝通
-
中央社 (2024.03) 印度當局:AI工具若未臻完善發布前須申請許可
-
中央社 (2023.12) 印度語言千百種 總理演說首次出動 AI 即時翻譯
-
中央社 (2023.11) 中正大學台印度 AI 團隊 啟動產官學研具體合作
-
中央社 (2023.05) 台印度資安專家研討會 聚焦 AI 運用防禦能力
-
國立中正大學 (2022) 開啟台印度跨國合作新篇章 中正大學永續智慧城市研究實驗室揭牌
-
國立中正大學 (2022.09) 建構智慧醫療國際網絡 中正大學「臺印度大數據分析實驗室」印度揭幕
-
國立中正大學(2024.04) 中正AI中心研發智慧交通科技打造永續智慧城市
-
駐印度台北經濟文化中心 (2022.09) 「臺印度永續智慧城市研究實驗室」揭牌儀式
-
新南向科研合作專網 (2022.03) 永續智慧城市建構:臺印 AI 人工智慧專家- 國立中正大學熊博安教授專訪
-
中央社 (2021.09) 四方安全對話峰會 美日印澳將同意建構安全半導體供應鏈
-
科技部 (2020.05) 防疫最前線臺灣與印度海外科研中心攜手創造合作新契機
-
國立成功大學前瞻醫療器材科技中心 (2019.12) 成大與全印度醫科大學簽訂首份合作協議 開啓醫療科技創新新里程
-
駐印度台北經濟文化中心 (2019.12) 成大與全印度醫學研究院簽訂首份合作協議
-
科技部 (2019.07) 科技部深耕新南向國家 補助中正大學於印度成立AI海外科研中心
-
駐印度台北經濟文化中心 (2019.07) 科技部補助中正大學在印度成立 AI 科研中心
